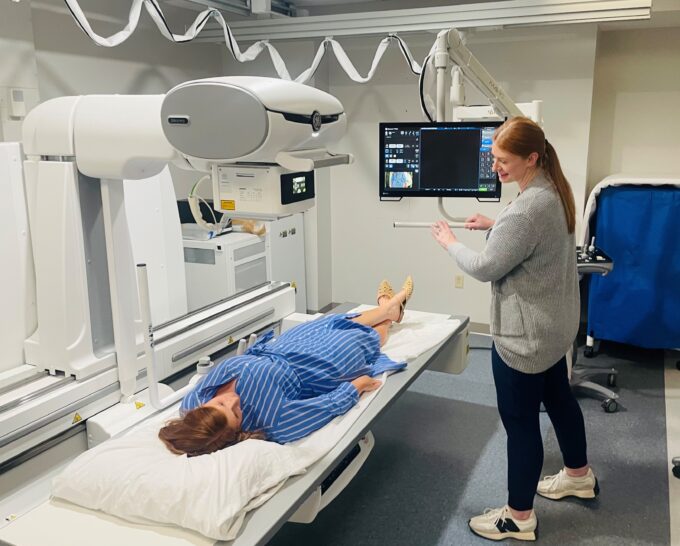
Diagnostic Radiology (X-Ray)
Radiography, more commonly known as X-ray, is the oldest and most frequently used form of medical imaging. Conventional diagnostic radiography uses small doses of ionizing radiation to produce diagnostic pictures of the human body. The image is created when the X-ray passes through bone and tissues onto a digital image recording plate. X-rays are commonly used to assist providers in the diagnosis and assessment of many conditions, including arthritis, bone fractures, pneumonia, and scoliosis.
There is no special preparation required for most radiographs. You may be asked to change into a gown for your examination, and you will need to remove any jewelry, eyeglasses, and any other metal objects that could obscure the images. Females should tell the doctor or technologist if there is any chance they could be pregnant. There is no pain associated with having an X-ray. Sometimes you will be asked to hold yourself in an uncomfortable position for a short time while the X-ray is taken, but that discomfort will be brief.
The images will be processed and the radiologist will interpret the study and promptly inform your referring provider of the results.
Digital Fluoroscopy
Fluoroscopy is real-time moving images that are produced using multiple X-rays captured on an image intensifier allowing our radiologists to see internal organs at work.
Common Fluoroscopy exams include Barium Swallows, Upper Gastrointestinal (UGI), Small Bowel, and Barium Enema examinations to diagnose disease in the esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines.
For people who are experiencing problems swallowing, GMC offers advanced swallow studies with a radiologist and speech therapist.
Bone Densitometry (DEXA Scan)
A bone densitometry scan is a simple, accurate and inexpensive way of detecting osteoporosis. This painless, advanced dual energy X-Ray can determine if osteoporosis is present in males or females. Osteoporosis doesn’t just impact elderly people. It’s a chronic condition that occurs when bone calcium and protein is depleted. Osteoporosis is characterized by low bone mass, increased bone fragility and increased risk of bone fracture
Bone DEXA scans are used to measure bone loss by scanning the spine, hip, and occasionally the forearm. Standard x-rays show changes in bone density after approximately 40% bone loss, while DEXA scans can detect bone loss after an approximate 1% change. By detecting the changes in bone loss, this technology can help estimate the risk for broken bones, as well as determine the need for treatment and monitor its effectiveness.
Computed Tomography (CT)
GMC offers advanced CT Scans, often known as CAT Scans, which are noninvasive, painless imaging tests that help physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions. CT imaging combines special X-ray equipment with sophisticated computers to produce multiple cross-sectional images or pictures of the inside of the body. This imaging technique is very sensitive and provides great clarity when studying internal organs, bone, soft tissue, and blood vessels, and reveals more details than regular X-ray exams.
GMC’s CT Scanner offers 3D multi-slice technology for more detailed images of structures inside the body including the head, chest, abdomen, spine, pelvis, extremities, and specialized imaging of the heart and coronary arteries.

Granville Medical Center’s CT program employs stringent dose reduction guidelines for adult and pediatric CT. As well, GMC follows special protocols that ensures the safety of our patients when IV contrast is required for their exam.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
GMC offers Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), which combines computer technology along with a strong magnetic field and radio waves to produce detailed images of the body’s tissues. Giant magnets allow your body to receive radio waves and “echo” them back. A computer uses the information within the echoes that bounce back from your body to create images.
The images created are unique to a patient, depicting his or her anatomy and any disease that may be present. The whole process is safe and painless. Some patients are so comfortable inside the magnet that they actually fall asleep while this advanced imaging takes place.
An MRI is most frequently done on an outpatient basis for those with suspected injuries. This procedure is painless, does not use radiation, and can be used for people of all ages to detect athletic or occupational injuries and strokes, or to diagnose certain diseases.
Screening and Diagnostic Services
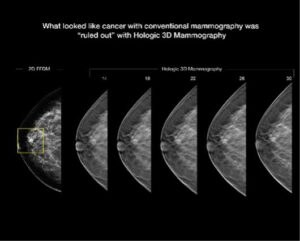
3D Mammography is the biggest breakthrough in breast imaging in 25 years. 3D technology allows our breast imaging radiologist to view breast tissue more clearly, increasing our chance of catching cancers even smaller than before. 3D mammography is performed in conjunction with a traditional 2D digital mammogram to create a more complete picture of breast tissue. During the 3D part of the exam, the X-ray arm sweeps in a slight arc over the breast, taking multiple images. A computer then uses these images to produce a layered 3D image of the breast tissue. This provides greater detail and allows the radiologist to see “inside” the breast layer by layer to find cancers earlier than ever.
Stereotactic breast biopsy imaging
Minimally invasive breast biopsy was developed in the 1980s.This technique allows for a highly accurate diagnosis through a small incision without the need for open surgery (other names for this type of biopsy are stereotactic biopsy, Mammotome biopsy, and vacuum assisted breast biopsy). A minimally invasive biopsy allows the tissue in question to be removed through a needle attached to a vacuum device. The needle is guided precisely to the abnormality using digital mammography. The needle placement is confirmed to be in accurate position by the images, assuring the highest accuracy possible. The vacuum allows the abnormal area to be sampled without disturbing the normal surrounding tissue. The tissue can then be examined by a pathologist to determine if cancer is present. A tiny marker clip may be placed at the time of the biopsy to mark the site of the biopsy. Most women are candidates for this minimally invasive breast biopsy and thus have options when selecting a biopsy procedure. The biopsy itself takes only 10-15 minutes–the whole visit typically takes less than an hour from start to finish, and women can usually return to normal activity immediately following the biopsy.
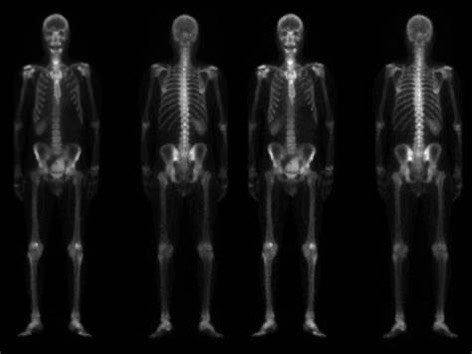
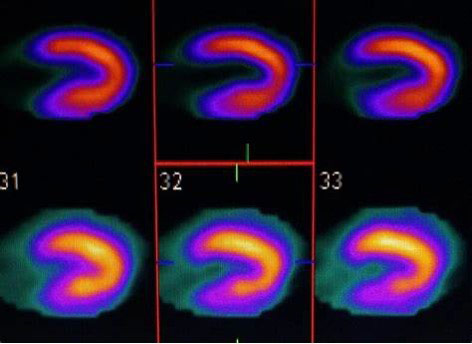
Nuclear Medicine
Nuclear Medicine imaging, in a sense, is “radiology done inside out” because it records radiation emitting from within the body rather than radiation that is generated by external sources like X-rays. In addition, nuclear medicine scans differ from radiology, as the emphasis is not on imaging anatomy, but on how the body part of interest is functioning. Nuclear medicine utilizes radiopharmaceuticals introduced into the body by injection, inhalation, or by swallowing. These radiopharmaceuticals aren’t dyes or medicine, and they have no side effects. The amount of radiation a patient receives in a typical nuclear medicine scan tends to be very low. After the radiation has had time to travel to the body part of interest, the imaging or scan begins.
Conditions diagnosed by nuclear medicine include:
- Blood disorders
- Thyroid disease, including hypothyroidism
- Heart disease
- Gallbladder disease
- Lung issues
- Bone problems, including infections and fractures
- Kidney disease
- Cancer
Ultrasound Services
A diagnostic ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging technique that sends high-frequency sound waves into the body to produce images of soft tissues and internal organs. Because ultrasound images are captured in real-time, they can show movement of the body’s internal organs as well as blood flowing through the blood vessels. Ultrasound enables the radiologist to make an accurate diagnosis of numerous medical conditions and diseases without the use of surgery or radiation by providing a clear window into the human body.
The ultrasound procedure involves passing a device called a transducer over the skin of the area to be examined. A series of images are produced and analyzed by an experienced radiologist. GMC routinely utilizes ultrasound equipment to produce high-quality images for medical diagnosis over a wide range of anatomical areas and clinical indications, including abdominal, obstetrics and gynecology, breast, thyroid, vascular, musculoskeletal, and other soft tissues of the body.
Echocardiography
An echocardiogram uses sound waves to produce images of your heart. This common test allows a Cardiologist to see your heart beating and pumping blood. A Cardiologist can use the images from an echocardiogram to identify heart disease, check for problems with the valves or chambers of your heart, check if heart problems are the cause of symptoms such as shortness of breath or chest pain, and detect congenital heart defects.
All Imaging services can be scheduled by appointment Monday – Friday from 8:00am – 5:30pm.
For more information call 919-690-3420. Fax Number: 919-690-0114